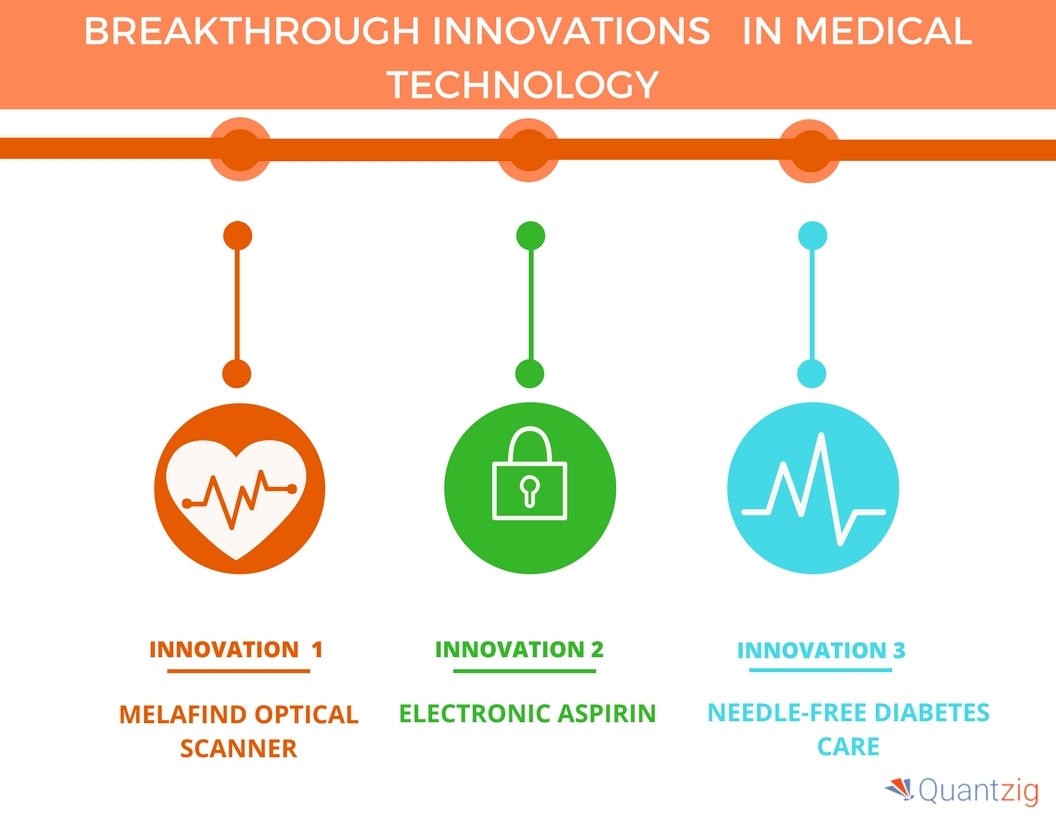
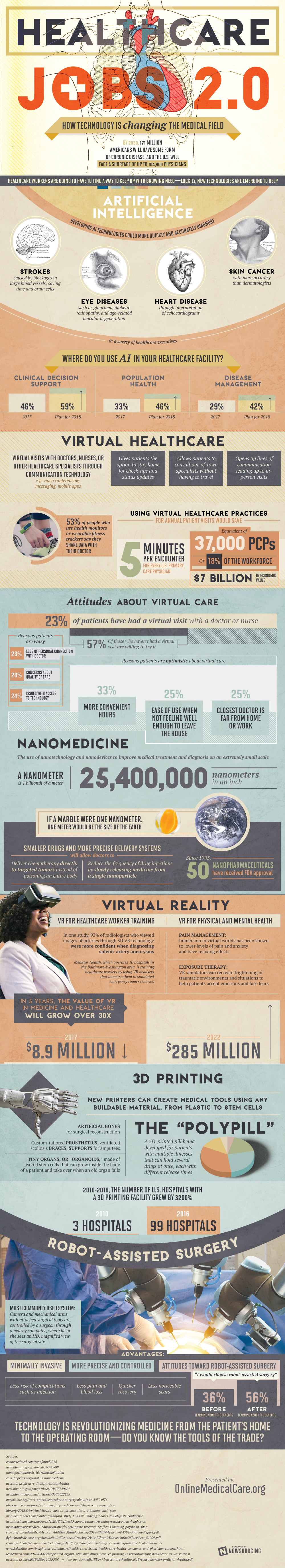
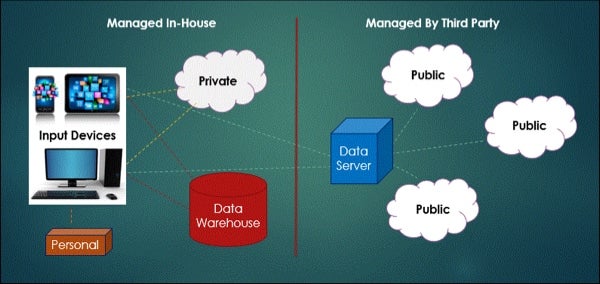
Providers have been slow to adopt EHRs because of their cost complexity and need for a fully developed infrastructure. Why has EHR adoption been so slow.
 Question 9 4 Out Of 4 Points Ehr Adoption Has Been Slow As A Result Of Selected Course Hero
Question 9 4 Out Of 4 Points Ehr Adoption Has Been Slow As A Result Of Selected Course Hero
Information systems have been making a noticeable entrance in the healthcare although their adoption has been slow.

Ehr adoption has been slow as a result of. The lack of readiness causes the weakness within the organization and to undergo transformation during the implementation of the EHRs. The results showed that 15 of US. Adoption and effective use of EHRs has been slow however in large part due to shortcomings with early generation EHRs that were and frequently remain poorly optimized to support efficient and effective clinical work provided by physicians and other clinicians.
The results showed that 15 percent of US. The adoption of EHRs by US. Thats a 50 jump in adoption -- but the US.
The physicians have the main role when using the EHRs since they are the ones who provide most of the information that the system handles within their automated processes. Hospitals had implemented a comprehensive EHR and an additional 76 percent had a basic EHR in place. Hospitals had implemented a comprehensive EHR and an additional 76 had a basic EHR in place.
Otherwise EHR adoption rates among small practices will remain relatively low and time horizons for complete adoption will remain distant. Further physicians and hospital systems had. This is because of a number of barriers including resistance to change initial difficulty in implementing a new system and lack of knowledge to plan a successful system transition.
Adoption rates of EHRs were similar between public and private institutions. Providers want to ensure the confidentiality of. Perceived usefulness perceived ease of use.
Larger hospitals major teaching hospitals and urban hospitals were more likely to have EHRs. Adoption rates of EHRs were similar between public and private institutions. Practices has been slow despite the perceived benefits of their use.
Other factors have also been cited as contributors to the slow adoption of EHR which include the unstable supply of electricity which makes the systems unreliable to the users. This paper examines the factors influencing the electronic healthcare records EHR adoption by modeling behavioral intention of physicians towards EHR adoption. A recent anecdote presented at the ONCs HIT Standards Committee Implementation Workgroup based on the experience of a Family Medicine physician early-adopter using a NextGen product described a 50 loss in productivity that lasted about 6 months and only slowly re-approximated pre-EHR levels after a year.
Interoperability has been slow to advance as EHR adoption has accelerated 38 and as a result interoperability has become a focal point of US policy efforts along with improving patient access to health data. Still lags Australia the Netherlands New Zealand Norway and the UK all of which have EHR adoption rates above 90. Small Nonteaching and Rural Hospitals Continue to be Slow in Adopting Electronic Health Record Systems Health Affairs.
Comparing the changes in the diffusion coefficients from the earlier period of measurement to the longer time span the external influence factor increased by 54 and the internal influence factor declined by 38. According to Meinert the slow rate of adoption suggests that resistance among physicians must be strong because physicians are the main frontline user-group of EMRs. The reason researchers from Drexel University focused on EHR implementation within ambulatory practices is due to the fact that health IT integration has been slow.
According to findings of a patient experience survey with EHR systems it was reported that physicians with EHR systems that meet meaningful use criteria felt that it provided time savings and resulted in enhanced confidentiality and less disruption in doctor-patient interactions. It hard to convert to digital. As a result clinicians are reluctant to adopt EHR World Health Organization 2006.
In fact growth in the basic EHR adoption rate between 2011 and 2012 was slower than may have been expected because there was little growth in one of the capabilities viewing imaging resultsthat isnt part of Meaningful Use until Stage 2. Larger hospitals major teaching hospitals and urban hospitals were more likely to have EHRs. Suresh Vishnubhatla executive vice president Long Term Operations for PharMerica says EHR adoption has been fairly brisk over the past 18 months based on the uptick his company is.
39 It is unclear how this shift in focus will be associated with entrepreneurship and overall HCIT investment although we might expect the nature of the technology to evolve to reflect these. The lack of readiness causes the weakness within the organization and to undergo transformation during the implementation of the EHRs. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology.
Moreover just 27 of American doctors said they had EHRs with multifunctional capabilities. Hospital Progress to Meaningful Use by Size Type and UrbanRural Location Health IT Quick-Stat 5. So having a basic EHR isnt necessarily a prerequisite for achieving Meaningful Use Stage 1.
Approximately 784 of office-based physicians use EHR systems while 481 of those work with a basic level EHR system.